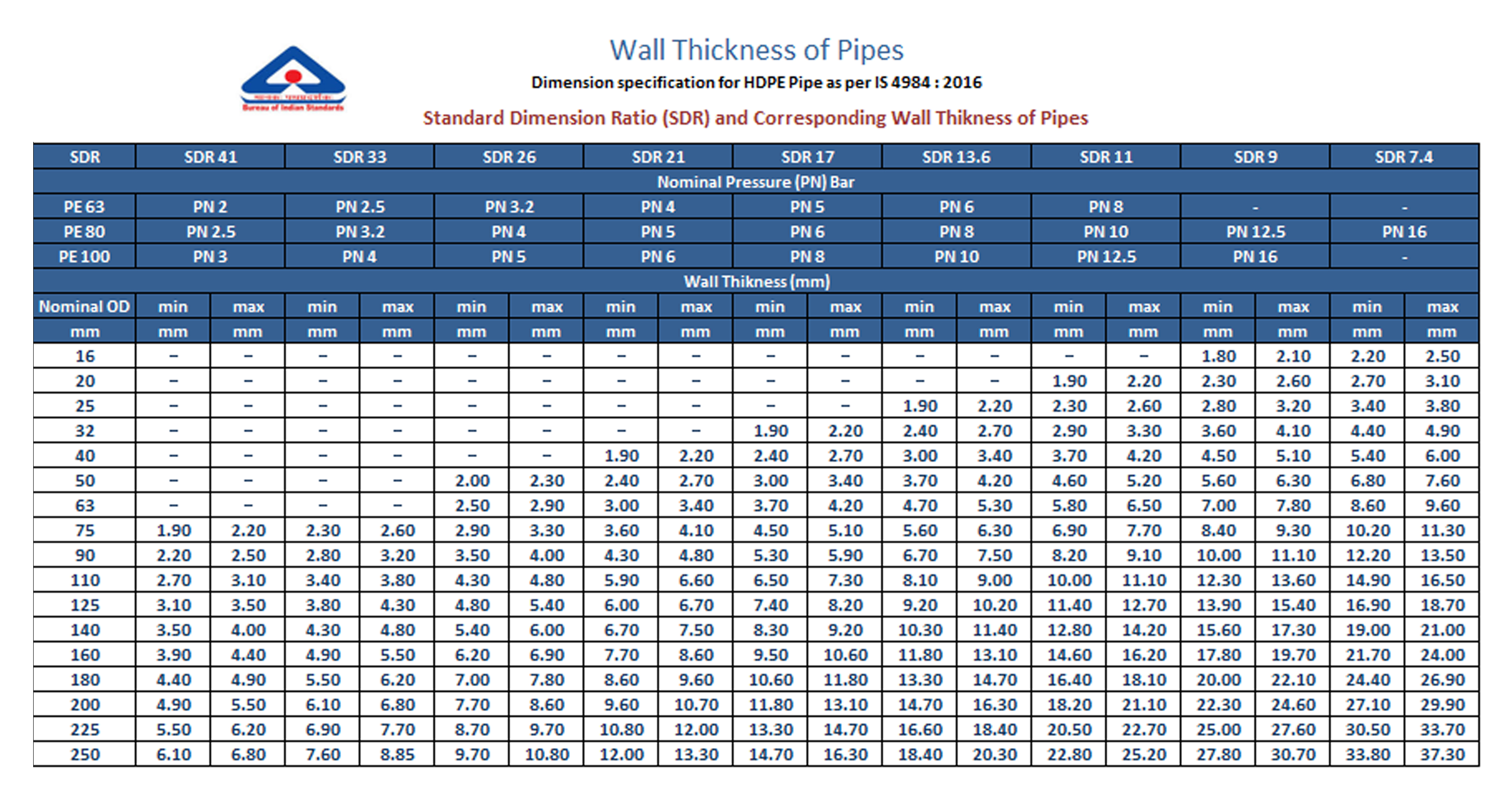
An Overview
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) or Polyethylene high density (PEHD) a polyethylene thermoplastic made from petroleum. With a high strength-to- density ratio, HDPE is used in the production of plastic bottles, corrosion-resistant piping, geomembranes, and plastic lumber. HDPE is commonly recycled, and has the number “2” as its resin identification code.
HDPE is known for its large strength-to-density ratio. The density of HDPE can range from 0.93 to 0.97 g/cm3 or 970 kg/m3. HDPE has little branching, giving it stronger intermolecular forces and tensile strength than LDPE. The difference in strength exceeds the difference in density, giving HDPE a higher specific strength. It is also harder and more opaque and can withstand somewhat higher temperatures (120 °C/ 248 °F for short periods)
The physical properties of HDPE can vary depending on the molding process that is used to manufacture a specific sample; to some degree a determining factor are the international standardized testing methods employed to identify these properties for a specific process.
HDPE leaks no toxic chemicals into the soil or water.